AFT Fathom Finds Optimization Opportunities in Hydrocarbon Separation Process
AFT Fathom™ Case Study
Sasol | Hydrocarbon Separation Plant | Oil & Gas

“…the model will be used on a continuous basis
for troubleshooting and evaluation of the plant’s
hydraulic health.”
– Nelius Joubert, Senior Operations Specialist
PROBLEM
- Hydrocarbon separation plant needed to be analyzed
- Both liquid and gas streams from extraction and distillation processes needed to be modeled
ANALYSIS
- AFT Fathom was used to model all unit operations
- The model was calibrated to match the measured plant data
SOLUTION
- Results were used to propose process control improvements
- Identified equipment that would need upgrading when production rates increase
Ready to try AFT Fathom?
Problem Explained
Nelius Joubert, senior operations specialist at Sasol, used AFT Fathom to model a complicated hydrocarbon separation plant in South Africa. The plant utilizes liquid extractants to separate the components of a liquid stream into separate pure components. This is done through a series of separation and purification steps in the plant, using extraction and distillation processes.
The process streams of the entire plant were simulated in AFT Fathom. The model contains 335 pipes and includes process feed streams from the storage tanks to the plant, all the streams in the plant that are used during plant operation, including internal recycle streams and product streams to the product storage tanks.
Tools & Analysis
Model creativity is demonstrated by the manner in which the liquid extraction and distillation columns are included in the model. Separate tanks were used to specify the different boundary conditions (fluid properties, pressures, and elevations) for each tie-off or tie-in to these columns.
AFT Fathom’s capability to simulate both vapor and liquid streams was used to create a continuous pressure envelope from the top of two of the distillation columns (vapor flow), through the vapor condensers and (liquid flow) into the reflux drums.
AFT Fathom also predicted the percentage opening of control valves, which were key in calibrating the model and identifying the fouled-up exchangers.
Solutions & Benefits
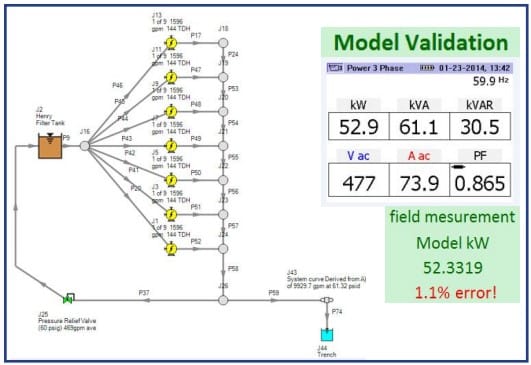
After completion of the model, it was calibrated to match the measured plant data. During this process, various plant problems (e.g. fouled heat exchangers, etc.) were identified that were listed for investigation or cleaning during the next plant shutdown.
The model was also used to propose improved control philosophies and other plant modifications to enhance its performance. Finally, the model was used to identify key pieces of equipment that would need to be upgraded should the plant want to increase production rates. In the future, the model will be used on a continuous basis for troubleshooting and evaluation of the plant’s hydraulic health.